Bridgestone Introduces the Third Generation of Run-flat TiresFor a Safer, More Environmentally Friendly Automotive Society
Tokyo (March 3, 2009) — Bridgestone Corporation today announced it has successfully developed new technologies and related it’s practical applications that improve the riding comfort of run-flat tires*1 Bridgestone will begin marketing this “third generation” of run-flat tires in 2009, focusing on sales to original equipment manufacturers for installation in new passenger vehicles.
As environmental awareness grows worldwide, automakers are accelerating the introduction of lighter, smaller vehicles. In response to that trend, Bridgestone is confident that its third-generation run-flat tires will significantly advance the use of run-flat tires by original equipment manufacturers, thereby accelerating the elimination of spare tires (emergency-use tires) in passenger vehicles. The company believes that further popularizing the safe and environment-friendly run-flat tires can make a major contribution to society.
According to Bridgestone, while there are various ways to eliminate spare tires the company believes that run-flat tires are the best way of eliminating spare tires because of significant advantages offered by them, including:
- Improved driving stability when the tire punctures
- Greater peace of mind as it avoids the need to change tires in dangerous places, such as on highways
- Continued mobility not only when punctures damage the tire tread in contact with the road surface, but even when punctures damage the tire sidewalls
Eliminating spare tires from all vehicles would help save resources by reducing the approximately 59 million*2 spare tires annually. Furthermore, CO2 emissions over the spare tire lifecycle—from raw material procurement to disposal—could be lowered by approximately 2 millions tons of CO2 per year.*3 Additional CO2 emissions can be reduced by the elimination of wheels for the spare tires.
By providing third-generation run-flat tires that realize such benefits, Bridgestone, as a company involved in the automotive industry, can contribute significantly to the creation of a car society that is safer and more environment-friendly.
*1 Run-flat tires are tires that can be driven on with zero inflation pressure for limited distance at reduced speeds. When used normally at 0kPa inflation pressure, they can be driven for up to 80km at 80km/h (ISO technical standard).
The run-flat (when inflation pressure is 0kPa) distance drivable of 80km is the distance drivable under test conditions based on ISO technical standard for technology. For the actual distance drivable, please refer to the owner’s manual.
*2 Bridgestone investigation
*3 Tire CO2 emissions are calculated in accordance with the Japan Rubber Manufacturers Association’s “Tire Inventory Analysis Trail” (1998 version). During the usage stage, emissions are considered to be zero.
Riding comfort comparable to that of conventional tires differentiates third-generation run-flat tires from those incorporating earlier technologies. A summary of these new products and explanations of the new technologies that enable them follows.
1. Summary of the evolution of third-generation run-flat tires
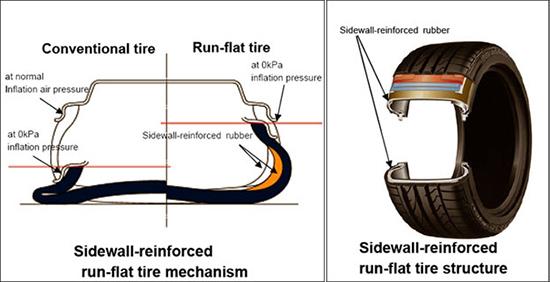
Bridgestone’s mainstay run-flat tires are those with reinforced rubber in their sidewalls. When Bridgestone started mass production of run-flat tires in 1987, the tires tended to give a hard ride comparable to conventional tires because the sidewalls were thick and somewhat inflexible. In 2005, Bridgestone introduced its second generation run-flat tire that featured improved riding comfort through an improved sidewall-reinforced rubber.
Bridgestone’s third-generation run-flat tires have adopted new technologies that further improve riding comfort. By application of these new technologies, the third-generation run-flat tires can reduce vertical stiffness deflection index* more than the second-generation run-flat tires and achieve riding comfort comparable to conventional tires. Moreover, they enable the development of run-flat tires in a wide range of sizes, including sizes that were previously difficult to develop.
*The tire functions as the spring absorbing a shock between a vehicle and a road surface.
The index of this case express the "strength of the spring".
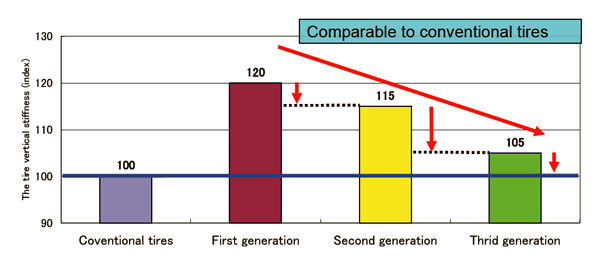
2. Summary of new technologies that enable the third generation
“Heat control” is the key to the technologies that enable third-generation run-flat tires. The simplest way to improve the riding comfort of sidewall-reinforced type run-flat tires is to make the tire sidewalls thinner and softer. However, when driving with a puncture, deformation of the tire sidewalls increases and generates more heat at that portion. How to deal with this heat generation while maintaining and increasing the durability of run-flat tires (after they lose inflation pressure), became a major challenge in efforts to improve riding comfort. In response, Bridgestone has developed three technologies to solve that puzzle: new sidewall-reinforced rubber that can reduce heat generation, a new ply that can reduce deformation growth, and COOLING FIN technology that can cool the tire sidewalls. Because each of these technologies improves riding-comfort performance separately, Bridgestone will select the technologies as appropriate when developing commercial products. (Based on tire sizes, the weight of the vehicles and when technologies become available for practical application.)
(1) New Sidewall-reinforced Rubber that Curbs Heat Generation
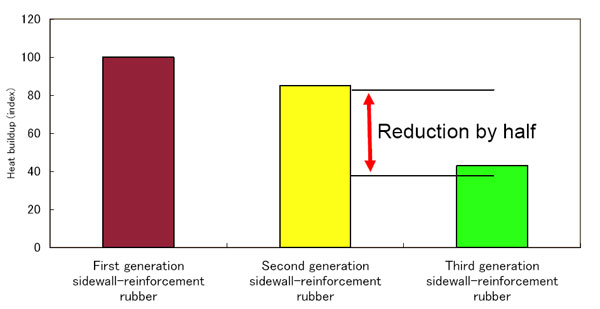
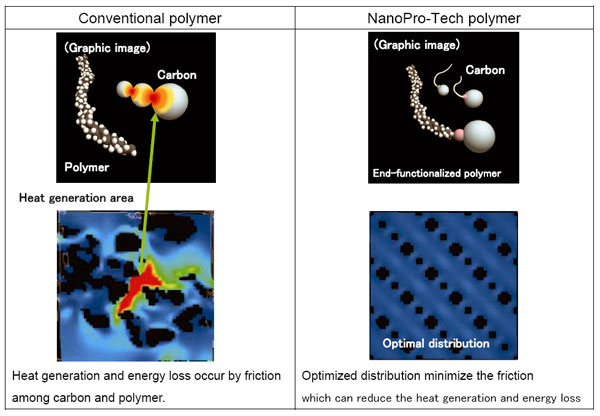
By adoption of NanoPro-Tech, we have created a new sidewall-reinforced rubber with improved carbon dispersion. The new rubber reduces the friction that occurs between carbon molecules when tire is loaded and reduces heat generation. Compared with second-generation sidewall-reinforced rubber, the new rubber can reduce by half heat generation due to deformation of tire sidewalls when driving on tires that have lost air pressure.
(a) Reduction of heat generation by new sidewall-reinforced rubber
(b) Summary of NanoPro-Tech Technology
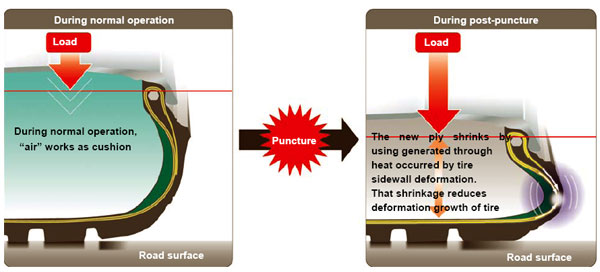
(2) New Ply (the tire body) that Uses Heat to Curb Deformation
The “new ply” is a new technology created by Bridgestone’s materials development technology that adapts a leading-edge fiber for use as tire material. When driving under run-flat conditions, the heat generated by tire sidewall deformation shrinks the new ply, thereby curbing deformation of the tire sidewall and preventing rapid increase in temperature.
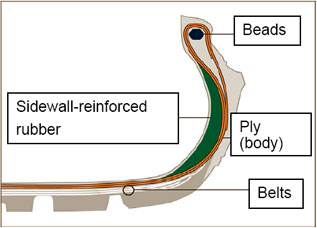
(a) Tire structure
(b) How new ply curbs tire deformation
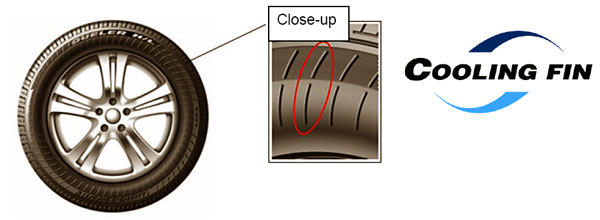
(3) COOLING FIN technology to Cool Tire Sidewalls
COOLING FIN is a technology that creates protrusions, which face toward the center of the wheel, on the surface of tire sidewalls in order to create disturbances in the airflow and thereby cool tires. The technology helps to cool the heat generated in tire sidewalls when driving on tires that have lost air pressure.
(a) Tire outer surface
(b) How COOLING FIN technology promotes airflow disturbance
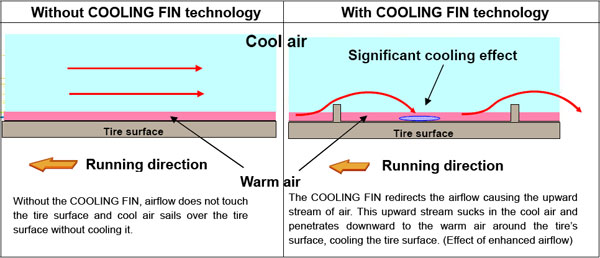
* The small dots represent airflow and the color of the dots represents the speed of airflow. Green or red-brown colored dots represent faster airflow than blue dots.
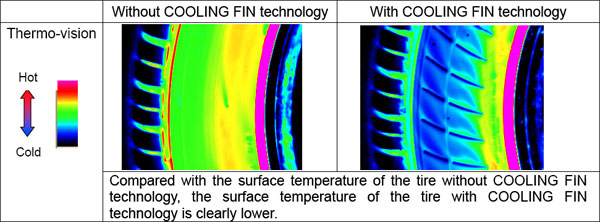
(c) The benefit of COOLING FIN technology: Comparison of tire sidewall surface temperatures
【Test using Bridgestone sidewall-reinforced type run-flat tires for SUVs (driving with 0kPa inflation pressure)】
{Reference data 1} The History of Run-flat Tires
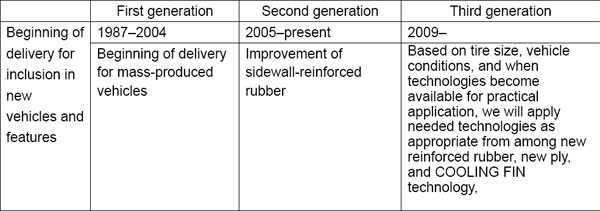
Bridgestone’s run-flat tire initiatives trace their origins to the early 1980s, when the Company began manufacturing tires that enabled vehicles for the physically disabled to be driven even after a loss of air pressure. In 1987, the selection of Bridgestone run-flat tires as a standard equipment for the Porsche 959 heralded the Company’s start-up of manufacturing for mass-produced vehicles. Since 1999, automakers have responded to society’s changing automotive needs by bringing more models to market with run-flat tire specifications. As a result—only twenty months after breaking through the 5-million-unit barrier in August 2006—Bridgestone’s cumulative shipments to automakers doubled, passing 10 million units in April 2008. Further, first-generation run-flat tires cover the period from 1987, when manufacturing for mass-produced vehicles began, until 2004. Second-generation run-flat tires cover the period from 2005, when improved sidewall-reinforced rubber enhanced riding comfort, until the present.
Breakdown of marketing periods by generation
{Reference data 2} Sidewall-reinforced type run-flat tires


Bridgestone Corporation,headquartered in Tokyo, is the world’s largest tire and rubber company. In addition to tires for use in a wide variety of applications, it manufactures a broad range of diversified products, which include industrial rubber and chemical products and sporting goods. Its products are sold in over 150 nations and territories around the world.

